This article throws light on Continuous Integration, the recent influencing technology of the software industry.
What is CI?
Continuous integration is a development practice in which the developers are required to commit changes to the source code in a shared repository, several times a day or more frequently. Every commit made in the repository is then built automatically which allows the team to detect the problems in advance.
The Traditional Method of the Deployment Cycle
The below image explains about the Traditional Method of the Deployment Cycle.
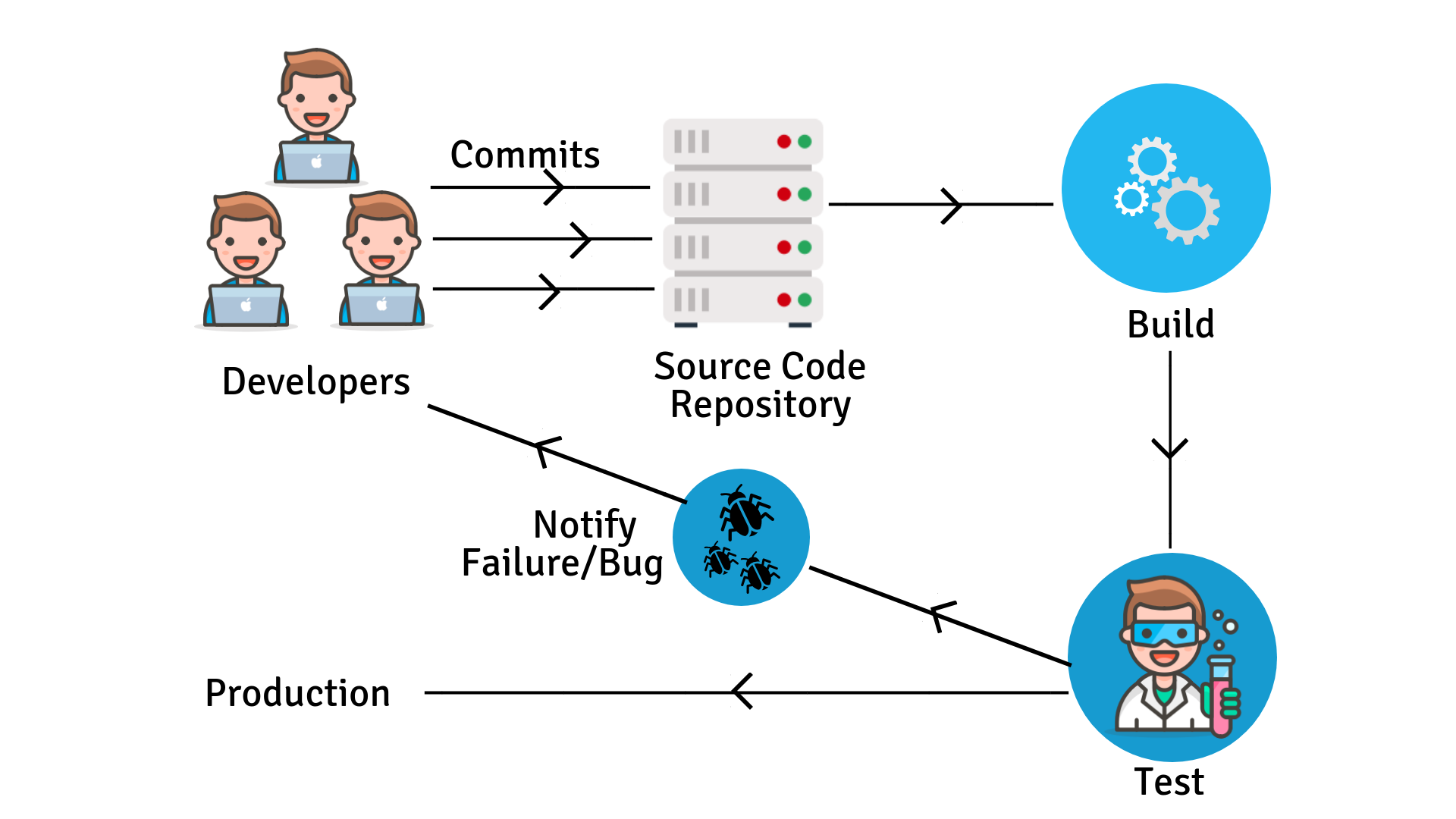
Disadvantages
- The developer should wait for test results until testing commences.
- Should walk through the entire source to locate a bug.
- Software delivery process is slow.
Deployment Cycle with Continuous Integration
The below image explains about the Deployment Cycle with Continuous Integration.
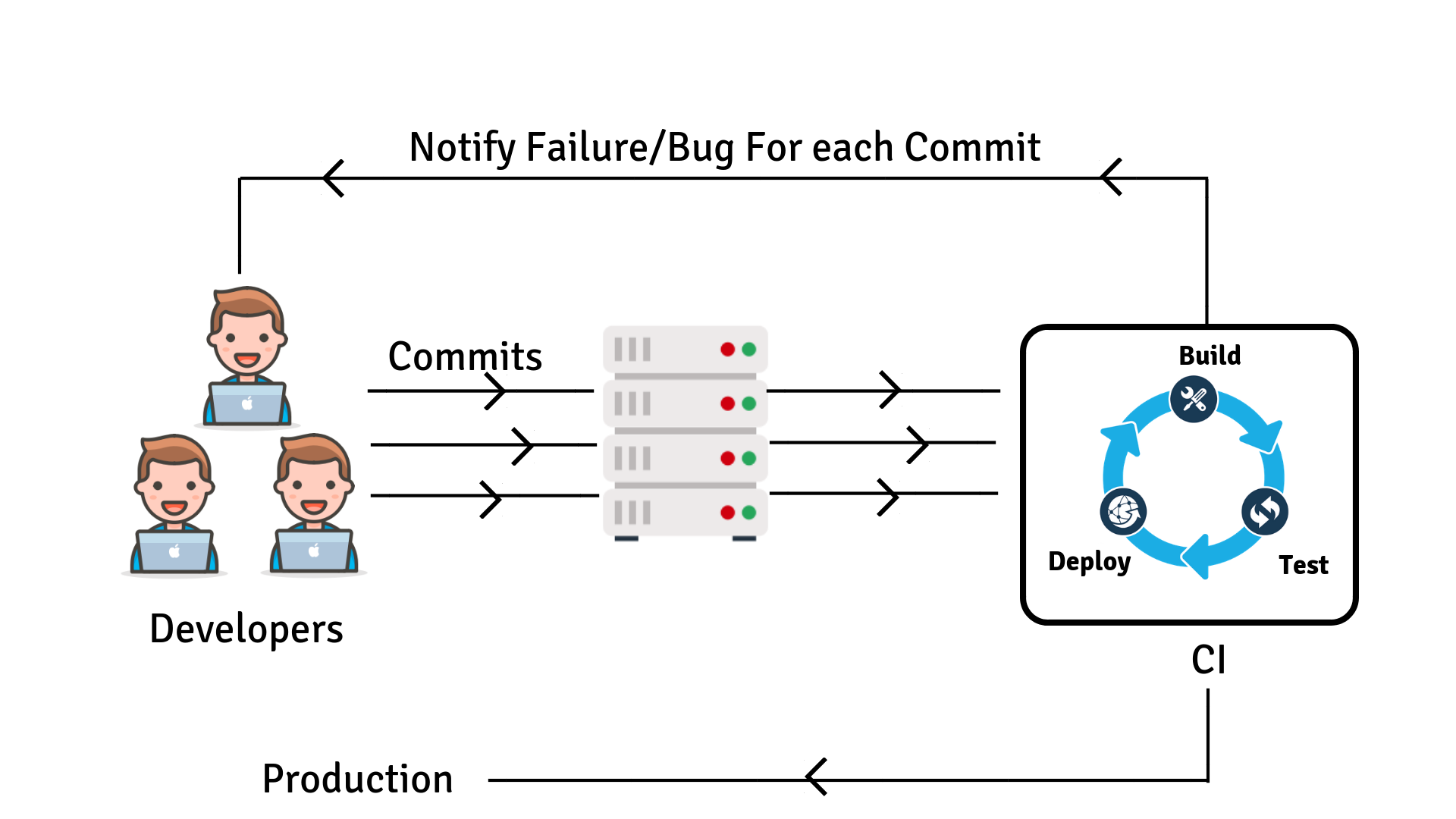 Advantages
Advantages
- After every commit to the source code, an auto build is triggered and is automatically deployed on the test server.
- If the test result reports a bug in the code then the developers have to check the last commit made to the source code.
- This also increases the frequency of new software releases.
- The concerned teams are always provided with relevant feedback.
Why We Need CI?
| Traditional Method | Continuous Integration |
|---|---|
| The entire source code is built and then tested | Every commit made in the source code is built and tested |
| Developers need to wait for test results | Developers know the test results of every commit made in the source code on the run |
| No timely Feedback | Feedback for every commit |
Few Popular Open Source CI Tools
- Jenkins
- Buildbot
- Travis CI
- Bamboo
Hope this blog turned out to be useful. Further articles about Continuous Integration using Jenkins are down the pipeline and do stay subscribed to get notified about those.
References







